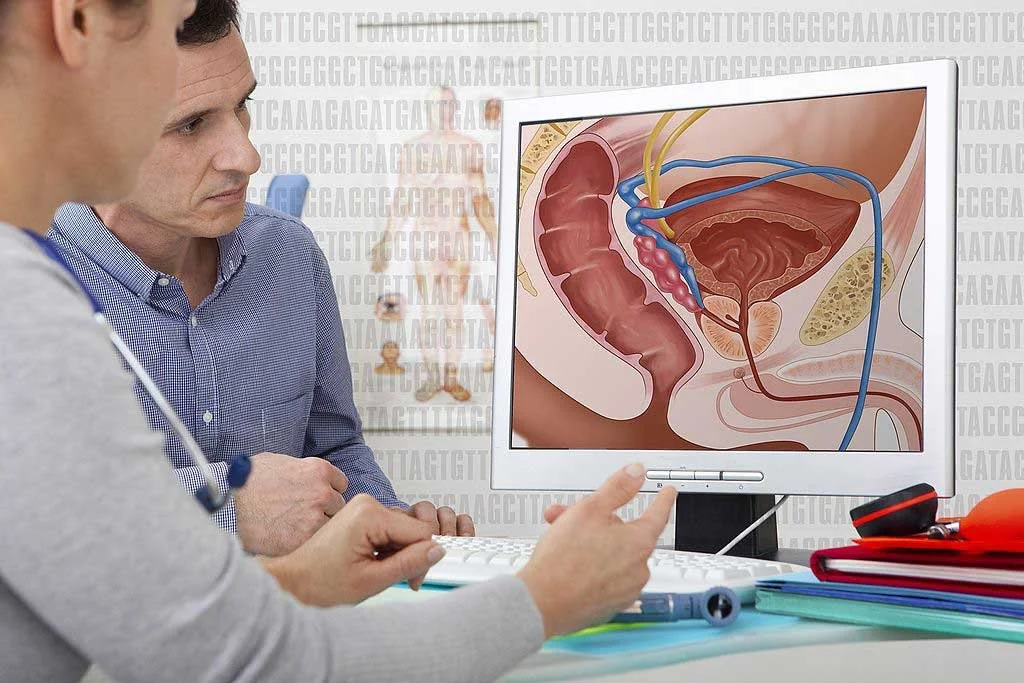
What is Enlarged Prostate?
The prostate is the semen-producing gland located below your bladder. An enlarged prostate simply means your prostate has grown larger, and this can cause problems with urination due to the location of the prostate. Although exact causes of enlarged prostate are unknown, aging and testosterone levels are major contributing factors to your likelihood of developing it.
Enlarged prostate is often called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). By age 60, roughly half of all men will have BPH and by age 85, about 90% of men will have it. Because of how common BPH is, symptoms of BPH can be ignored as natural aging processes. For this reason, many men will never seek treatment even though BPH can be treated with medication.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of BPH are problems with urination. You may feel the need to pee more frequently, and urinating may not feel as satisfying due to the bladder not emptying entirely. This is due to the pressure an enlarged prostate places on your urethra where it attaches to your bladder.
Urine remaining in the bladder for extended periods can increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) or bladder infections. UTIs can cause pain and more serious bathroom problems, as well as kidney infections if left untreated.
Treatments
Talk to your doctor if you experience any symptoms of BPH as outlined above, or if you have any other concerns around your urination. If your doctor finds that you have BPH, you may be given medication to reduce the size of the prostate. This relieves the symptoms within a few days for most men, and if you do not see improvements after a round of medication your doctor may recommend surgery to remove excess tissue.
Enlarged prostate is a common issue faced by most men as they age, but keep in mind that it can cause more serious problems if left untreated, and treatment is a simple way to return your bladder to working order.